Consider SEO automation as an advanced digital assistant that efficiently manages repetitive SEO tasks.
The goal is not to replace thinking. It is to preserve it. When routine operations run in the background, you keep attention on strategy, quality, and revenue.
In practice, automation should feel like invisible plumbing. Data flows in. Issues surface on their own. Reports arrive before the meeting starts.
Keep reading and you’ll see what SEO automation is and which parts of SEO it can handle best. You’ll also find out which tools make it possible and how to put it into practice step by step.
What is SEO Automation?
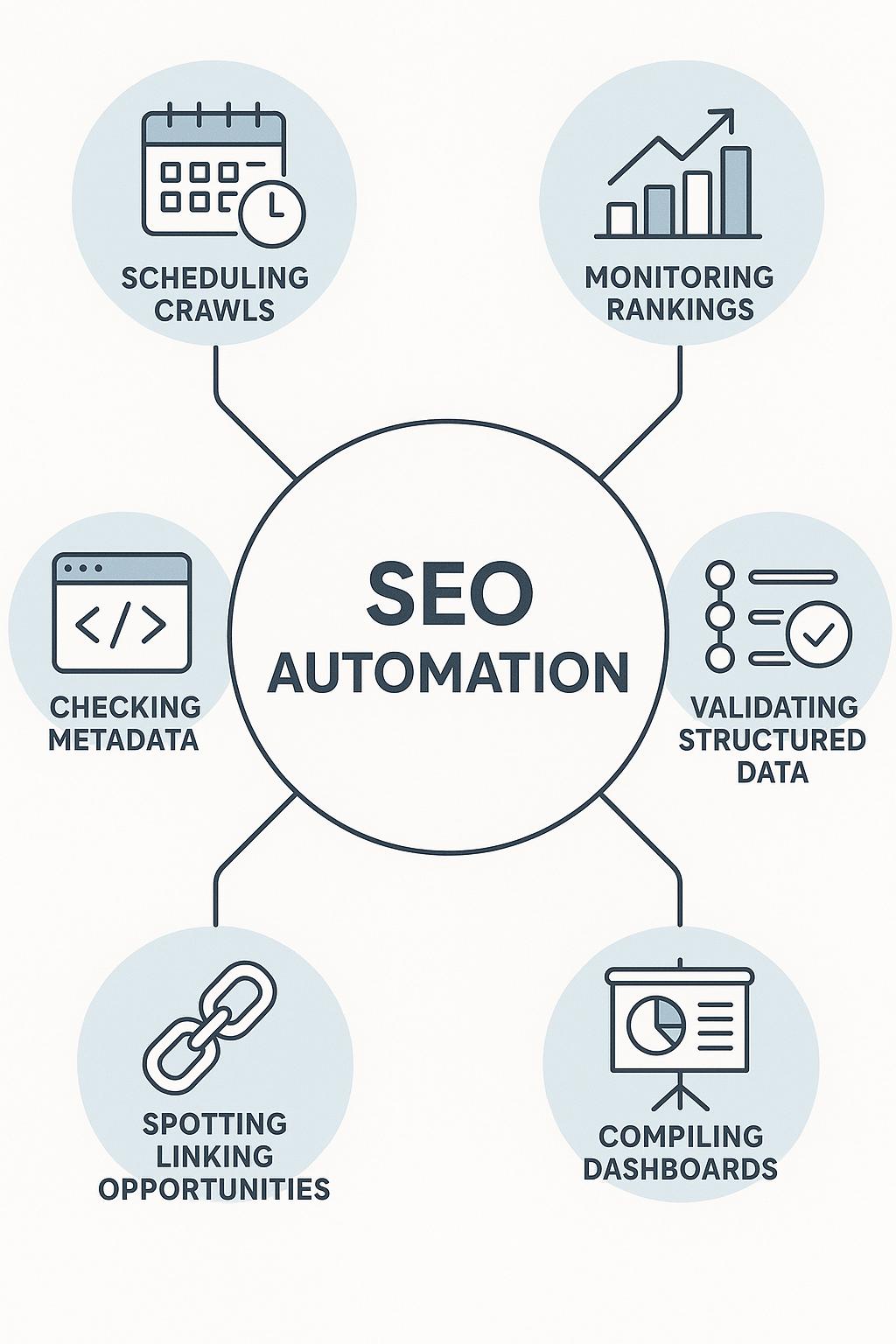
SEO automation is the practice of using software to perform search optimization tasks with minimal human input.
It includes:
- scheduling crawls
- monitoring rankings
- checking metadata
- validating structured data
- spotting linking opportunities
- compiling dashboards
APIs and connectors tie these steps together.
Crucially, the process still needs intent. Someone defines what to monitor, how to score risk, and when to escalate. Someone also vets content quality, brand voice, and legal constraints.
Automation handles the core tasks, but strategic decisions sit with people.
Teams usually design automated SEO workflows around repeatable triggers. For instance, a daily crawl flags 404s. A rank tracker alerts on big position drops. A change monitor pings when robots.txt or canonical tags change.
As a result, issues surface fast, and fixes ship before they snowball.
 Benefits of SEO Automation
Benefits of SEO Automation
Time savings is the headline, yet the real value is reliability. Machines do not forget to run checks on Friday afternoons.
Consistent monitoring reduces downtime, preserves rankings during releases, and limits revenue loss.
Automation also sharpens prioritization. When issues get risk-scored and grouped, teams fix high-impact items first.
Finally, centralized data improves alignment between SEO, product, content, and engineering.
Consider these practical gains:
- Fewer surprises during deployments due to pre- and post-release audits.
- Faster feedback loops on new pages, templates, and experiments.
- Clear documentation because dashboards and annotations live in one place.
SEO Tasks You Can Automate
Automation shines where rules are clear and volume is high. The following areas deliver quick wins without sacrificing judgement.
1. Keyword research and tracking
Research usually starts broad and narrows into intent clusters.
Automation helps gather volumes, group terms, and identify gaps at scale. It also tracks movement daily or weekly, segmented by device and location.
Here are a few ways to put it into practice:
- Set alerts when a query drops more than X positions or falls off page one.
- Group terms by intent and funnel stage to match content types.
- Use query lists to watch competitors and new SERP features that displace classic results.
Longer phrases (long-tail keywords) are easier to qualify and convert. Additionally, difficulty scores can guide prioritization, though they are directional.
2. On-page SEO checks (meta tags, headings, alt text)
On-page quality assurance (QA) is perfect for automation.
Crawlers can flag missing titles, duplicate H1s, thin word counts, long slugs, or missing alt attributes. Templates can insert fallback meta tags where content teams miss fields.
But, on-page work is not only compliance. Titles need purpose. Intros must satisfy the query.
Therefore, run automated checks first, then tighten drafts with a short editorial pass. When teams publish at volume, this two-step rhythm protects quality.
3. Technical audits (site speed, structured data, etc.)
Technical health drifts over time. New scripts slow pages, releases break canonical tags, and caches get misconfigured. Scheduled audits find this drift before users feel it.
Here are a few checks worth automating:
- Track Core Web Vitals on key templates with PageSpeed Insights, and set alerts when metrics slip below healthy thresholds.
- Validate schema types with a crawler and confirm properties against Schema.org.
- Run pre-release crawls on staging. Then, run a focused crawl after the deployment to compare changes.
In one migration, a team caught invalid hreflang on 60 locale pages before launch. Consequently, they preserved stable indexing and avoided weeks of cleanup.
4. Link management
Links shift constantly. Pages get deleted, redirects change, vendors retire subdomains.
Automated checks should verify internal links, redirect chains, and rel attributes weekly. Change monitors can track partner pages and high-value referring domains.
Internal and external linking play a key role in SEO by guiding users and search engines through your content. AI tools such Stryng makes it effortless by automatically spotting opportunities and adding links with just a few clicks:
If a link from a core nav item breaks, product should get the alert. For backlink health and index coverage, route technical flags to the SEO owner and surface the rest in Google Search Console.
5. Rank tracking and reporting
Rank tracking answers three questions: where pages sit today, how they moved, and why. Automation handles the first two. To get the third, add annotations for releases, content updates, and algorithmic swings.
- Track by device, market, and page type to avoid noisy averages.
- Segment by SERP feature so you see when a featured snippet replaces a classic result.
- Send weekly digests to stakeholders and a detailed view to the core team.
Additionally, pair rankings with click, impression, and conversion data. That way, you do not chase vanity swings that never reach revenue.
Best Tools for SEO Automation
There is no single stack for every team. Choose categories that fit maturity, traffic mix, and headcount.
The table below compares common tool types. Pricing changes often, so focus on use cases and integration fit.
| Category | What it automates | Good for |
|---|---|---|
| All-in-one suites | Keyword research, rank tracking, site audits | Small to mid teams that want breadth |
| Crawlers | Large-scale audits, on-page checks, structured data | Sites with many templates or frequent releases |
| Change monitoring | HTML diffs, robots.txt, canonicals, redirects | Release-heavy teams |
| Log analysis | Crawl budget, status codes, bot behavior | Enterprise, international SEO |
| Content optimization | NLP scoring, topical coverage, briefs | Content-heavy programs |
| Reporting/BI | Dashboards, alerts, annotations | Cross-team visibility |
SEO automation often runs through established platforms.
Semrush handles audits and keyword tracking. Ahrefs focuses on backlink data. Moz covers monitoring and reporting. They are not focused on strategy or content; their core strength is data and reporting.
For those who want to bring content production, branding, and editorial quality into one integrated workflow, Stryng is a smart choice.
Consider combining these tools according to your priorities and business size for best results.
Risks and Limitations of SEO Automation
Automation introduces its own failure modes. Knowing them upfront keeps programs healthy.
- Over-reliance on scores. NLP grades and difficulty scores are directional. They do not replace research or user interviews.
- False positives and negatives. Crawlers can miss dynamic content. Alerts can misfire on timing or localization. Therefore, maintain manual spot checks.
- Quality dilution. Auto-generated content can read generic without editorial craft. If you scale drafts, run a humanization pass and match brand voice.
- Policy drift. Search guidelines evolve. Keep an eye on Google Search Essentials and adjust templates as rules change.
- Privacy and security. APIs move data across stacks. Work with IT on access control, PII handling, and vendor risk.
If you publish AI-assisted content, review this cautionary take on AI-generated content SEO risks. In short, automation speeds work, but human oversight protects trust.
How to Implement SEO Automation Effectively
A phased approach works best. Start with guardrails, then scale.
- Define outcomes. Decide what success looks like: fewer critical errors, faster content cycles, or revenue from organic. Tie each goal to a metric and owner.
- Map workflows. List manual steps for research, publishing, and QA. Then mark steps that follow rules. Those become automation candidates.
- Pick a lean stack. Choose one crawler, one rank tracker, and one reporting layer. Avoid overlapping tools early.
- Standardize naming. Agree on URL patterns, content types, and tracking tags. Consistent naming makes filters and dashboards reliable.
- Set thresholds and SLAs. Decide which alerts are critical, who gets them, and how fast they must act.
- Automate content planning. Use reusable briefs and a content calendar with clear dependencies.
- Protect quality. Add a human pass for voice and clarity. If drafts come from AI assistance, run a quick humanization and bias check before publishing.
- Annotate changes. Record releases, outages, and experiments in your rank and traffic dashboards. Without context, trend lines mislead.
- Review quarterly. Retire noisy alerts and expand automation into programmatic SEO where templates perform well.
- Invite the business in. Share simple, visual reports. As stakeholders see progress, budgets follow.
Summary
- SEO automation saves time on monitoring, analysis, and reporting, so strategic work gets done.
- The smartest stacks combine crawlers, rank trackers, and content QA, plus clear guardrails.
- Start small. Automate high-frequency tasks with clear rules, then scale to complex workflows.
- Automation does not fix weak content. Editorial standards, UX, and brand voice still rule.
- Always pair scheduled checks with human reviews to avoid false positives and costly errors.
- Track changes and annotate releases. Otherwise, you will not know what moved the needle.
- Treat tools as teammates. Configure alerts, thresholds, and ownership to prevent alert fatigue.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is SEO automation suitable for small teams?
A: Yes. It helps small teams cover more ground with fewer tools. Start with a crawler, a rank tracker, and a simple dashboard. As needs grow, add change monitoring and content QA. Keep ownership clear to avoid alert fatigue.
Q2: Can automation handle programmatic SEO?
A: It can support it. Templates, feeds, and scheduled publishing work well when rules are tight. However, invest in quality checks and safe release processes. Programmatic SEO still needs human reviews to avoid duplication or thin pages.
Q3: Which metrics matter most for automated reporting?
A: Track organic revenue or qualified leads first. Then watch impressions, clicks, and rankings by intent group. Include Core Web Vitals and error counts for technical health. Add annotations for releases so trends make sense.
Q4: How does automated SEO workflows affect content quality?
A: Workflows free editors to focus on clarity and usefulness. They also enforce metadata and schema consistency. Even so, every draft should get a human pass for voice, accuracy, and originality. That balance keeps content competitive.
Q5: What should be avoided when scaling technical SEO automation?
A: Avoid unvetted rules that mass-edit tags. Do not skip staging checks. Limit access to production settings. Additionally, rotate periodic manual audits to catch gaps automation misses. Thoughtful controls prevent costly mistakes.



